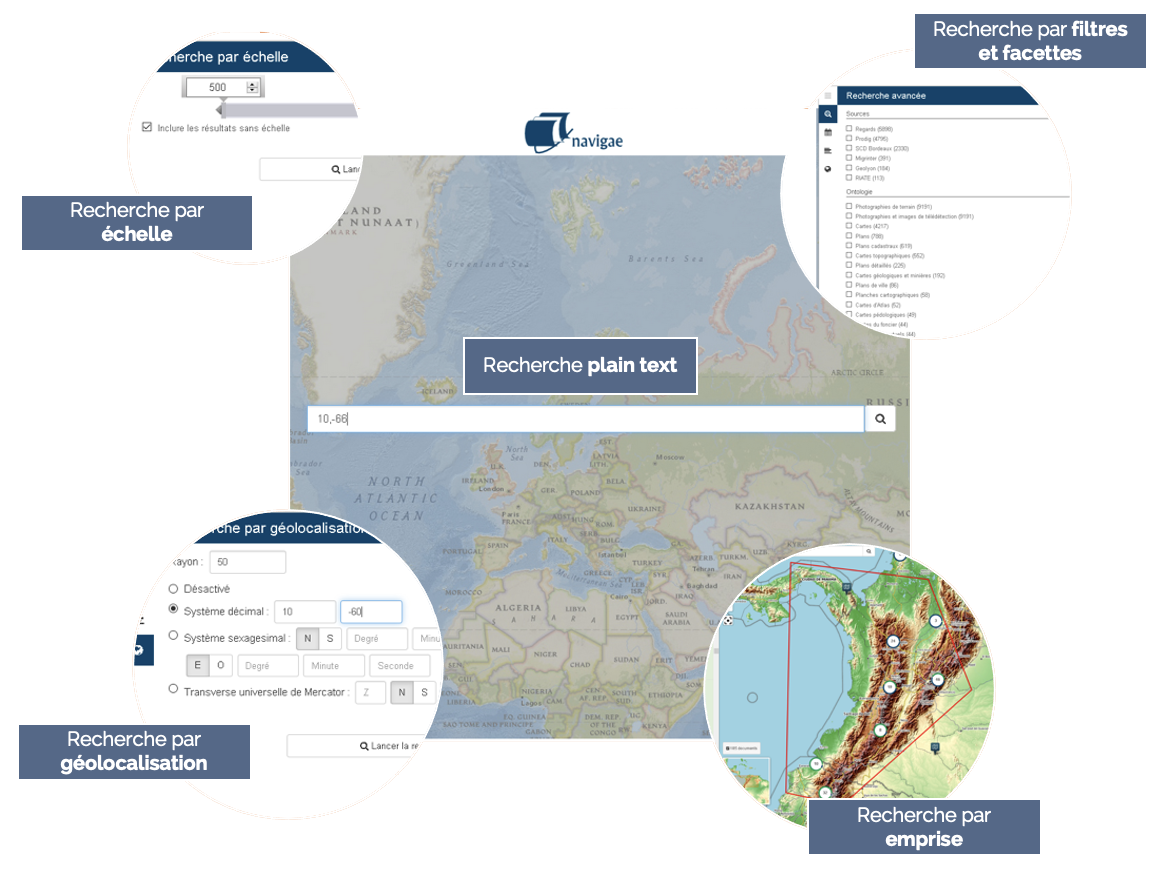
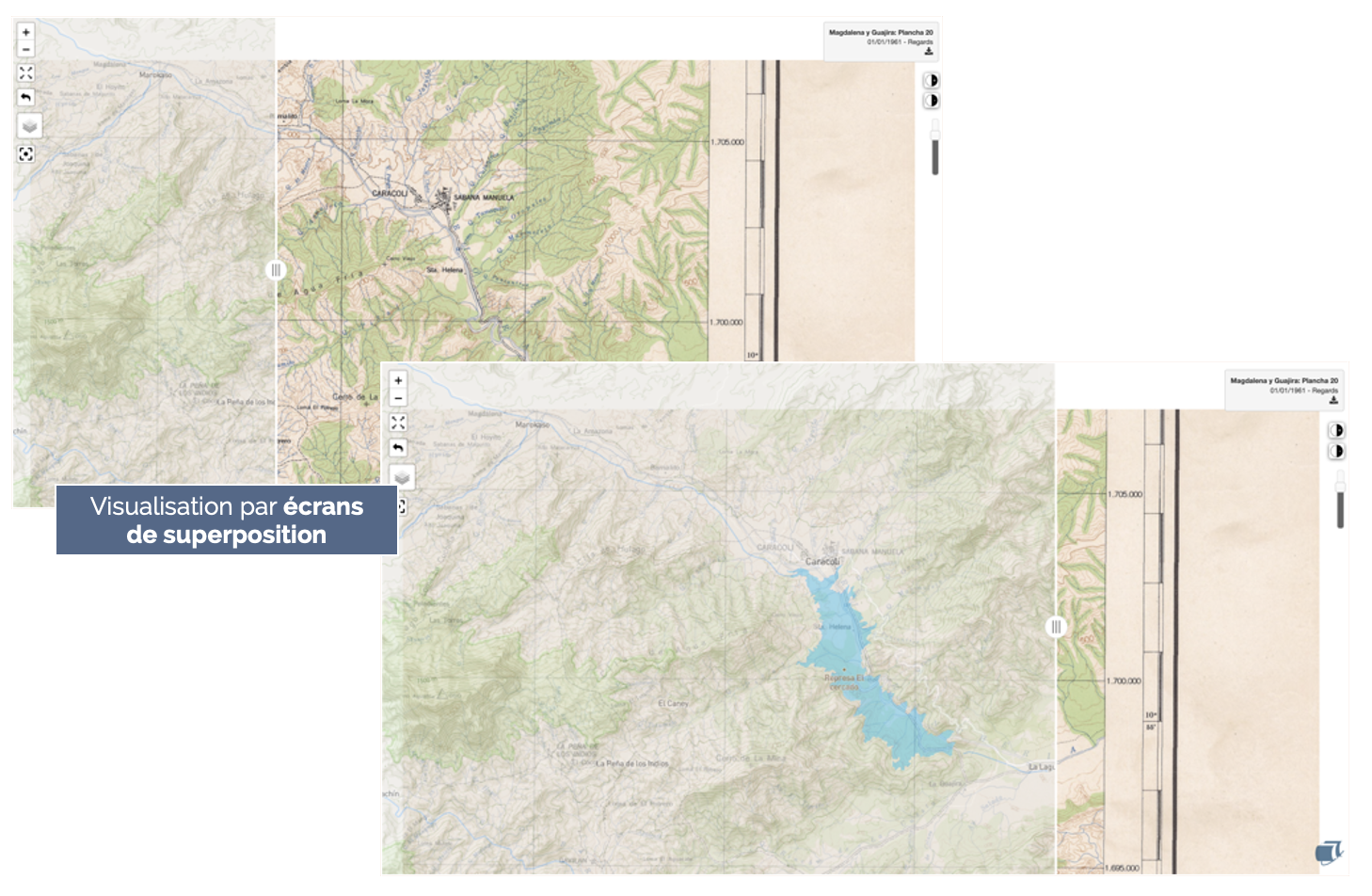
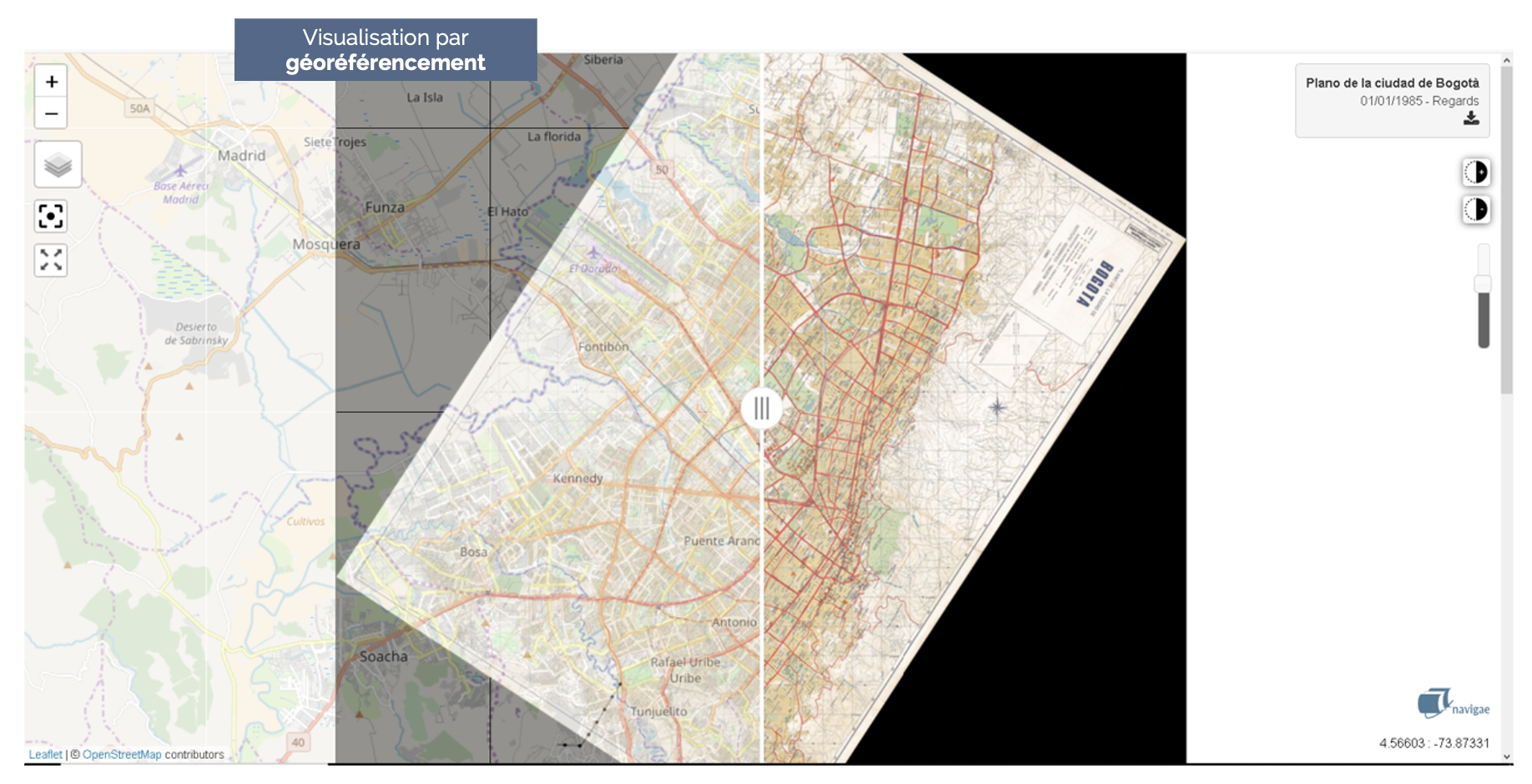
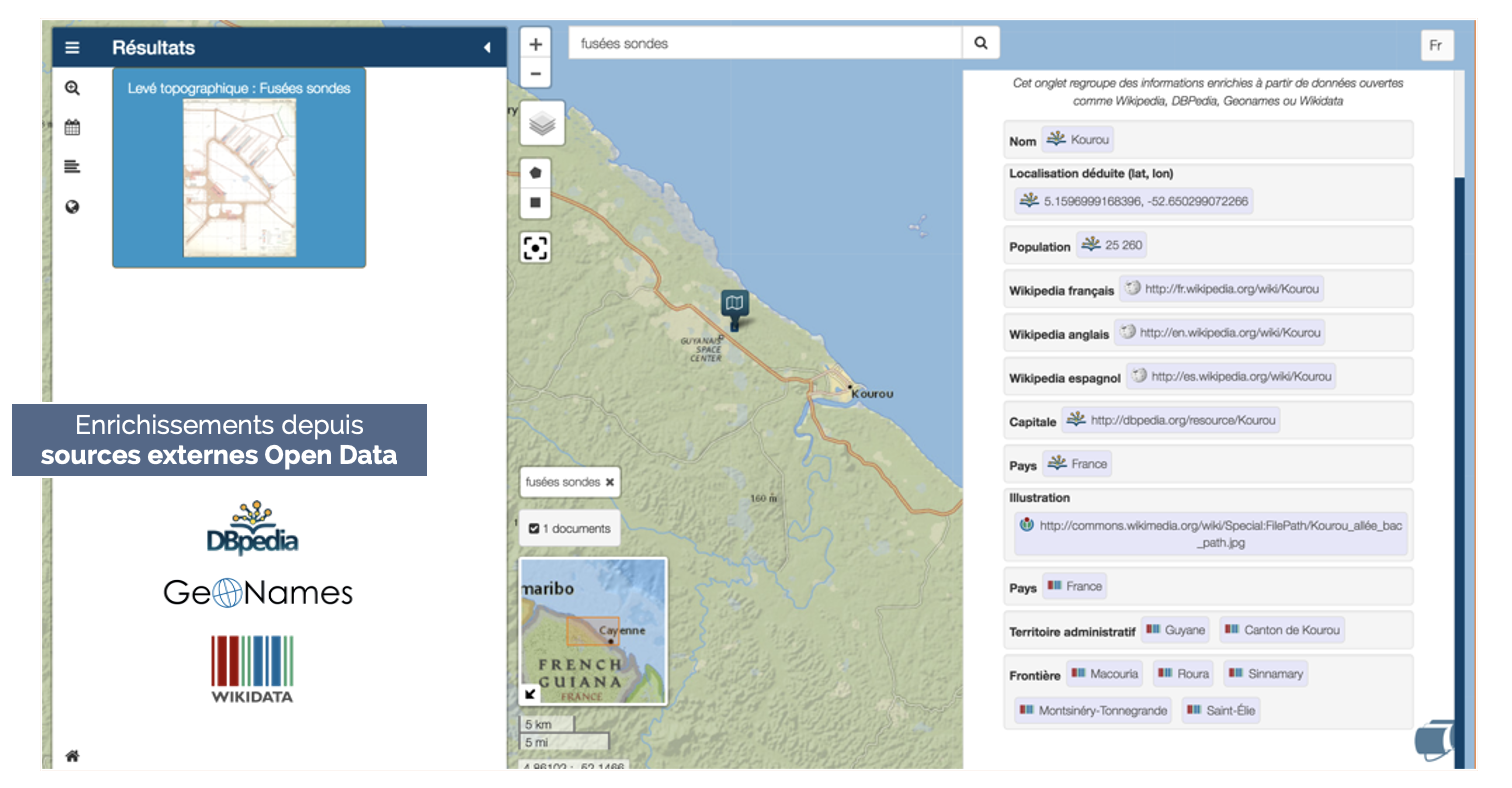
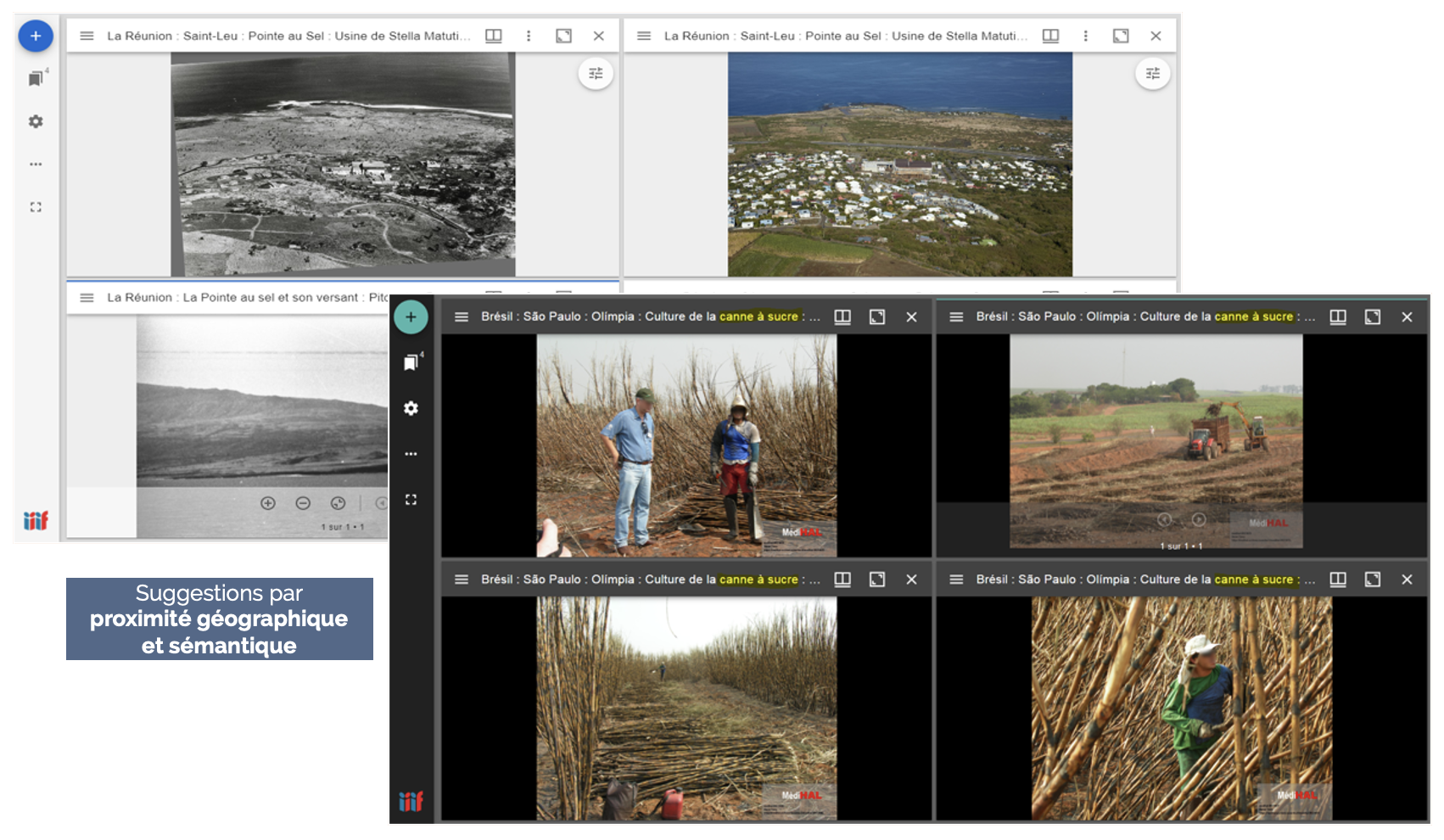
Our work
Discover our latest projects implemented using our solutions
FOXCUB DATA PLATFORM and FOXCUB AI PLATFORM,
as well as our recent collaborations.
FOXCUB DATA PLATFORM and FOXCUB AI PLATFORM,
as well as our recent collaborations.
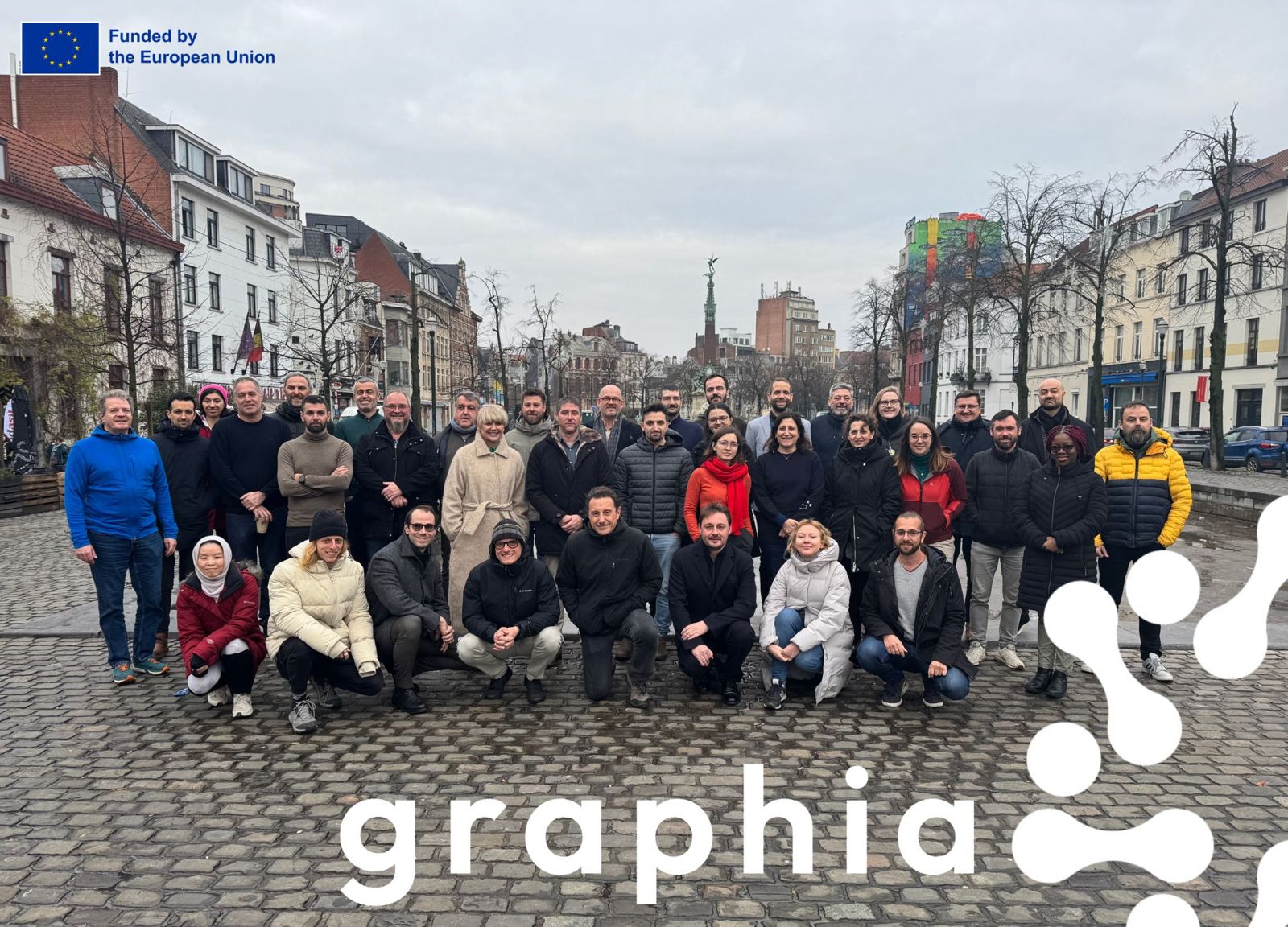
GRAPHIA

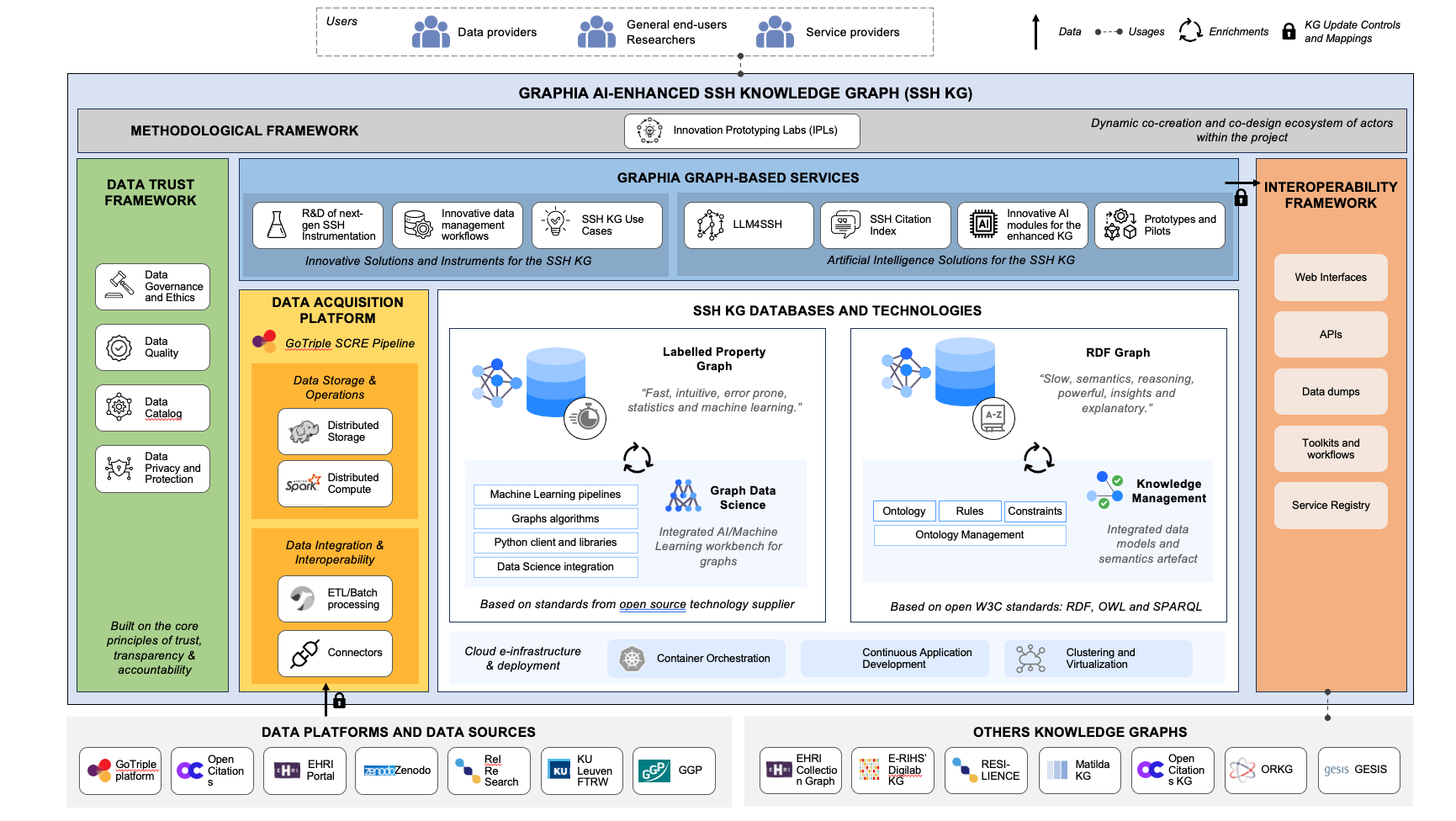
GRAPHIA is a major European project aiming to equip the social sciences and humanities (SSH) with a knowledge graph enriched by artificial intelligence. In collaboration with OPERAS, the CNRS, GESIS, TIB, CNR, and other key infrastructures, Foxcub contributes to the development of hybrid RDF/LPG architectures, advanced AI services, and an open ecosystem for the reuse of SSH data.
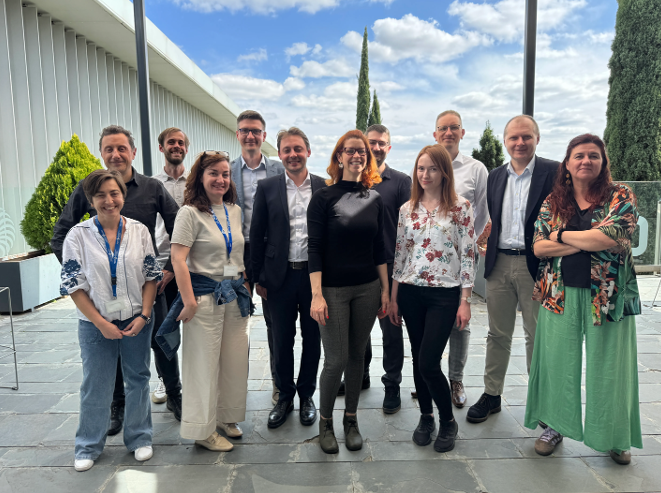
LUMEN

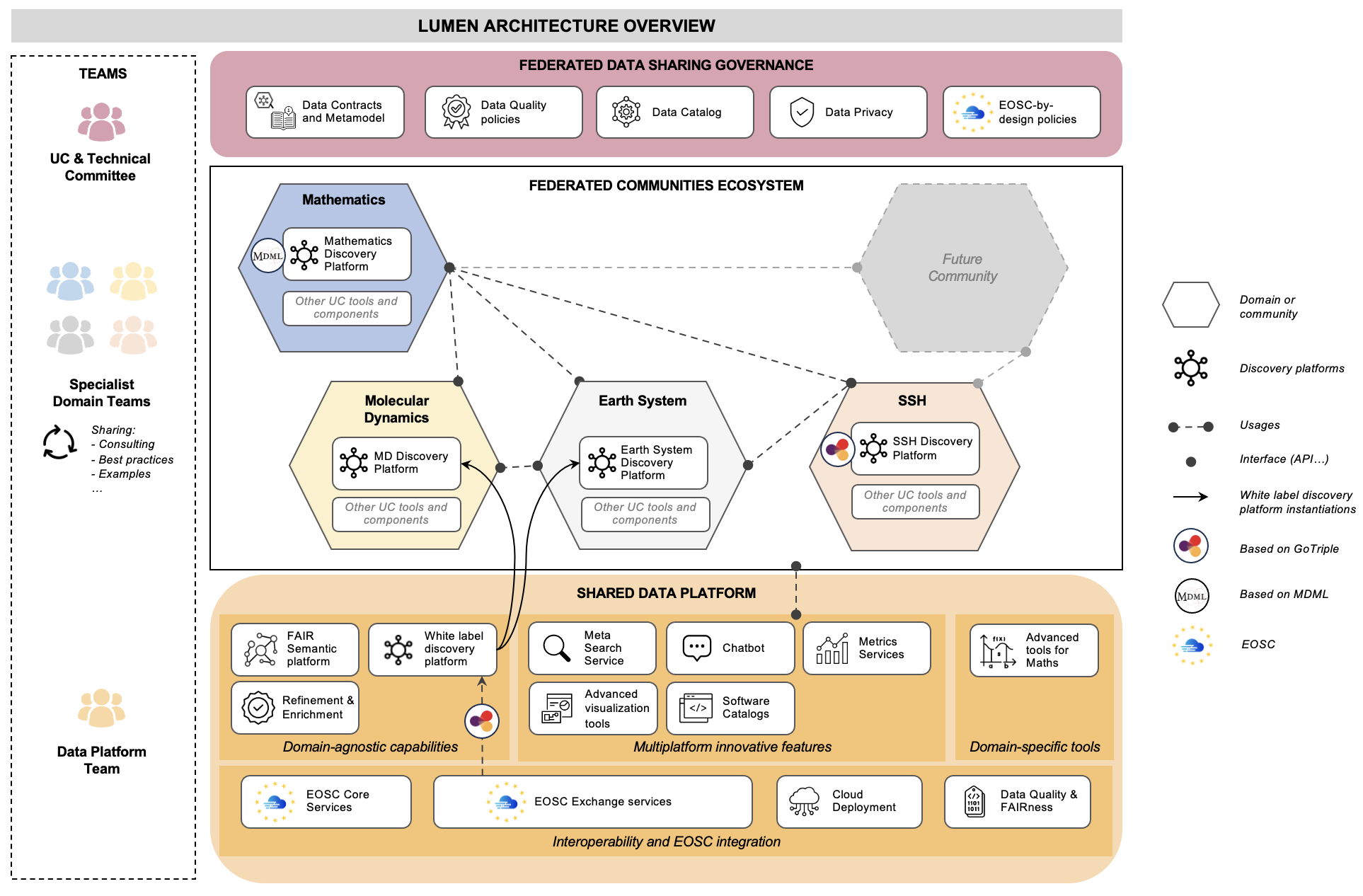
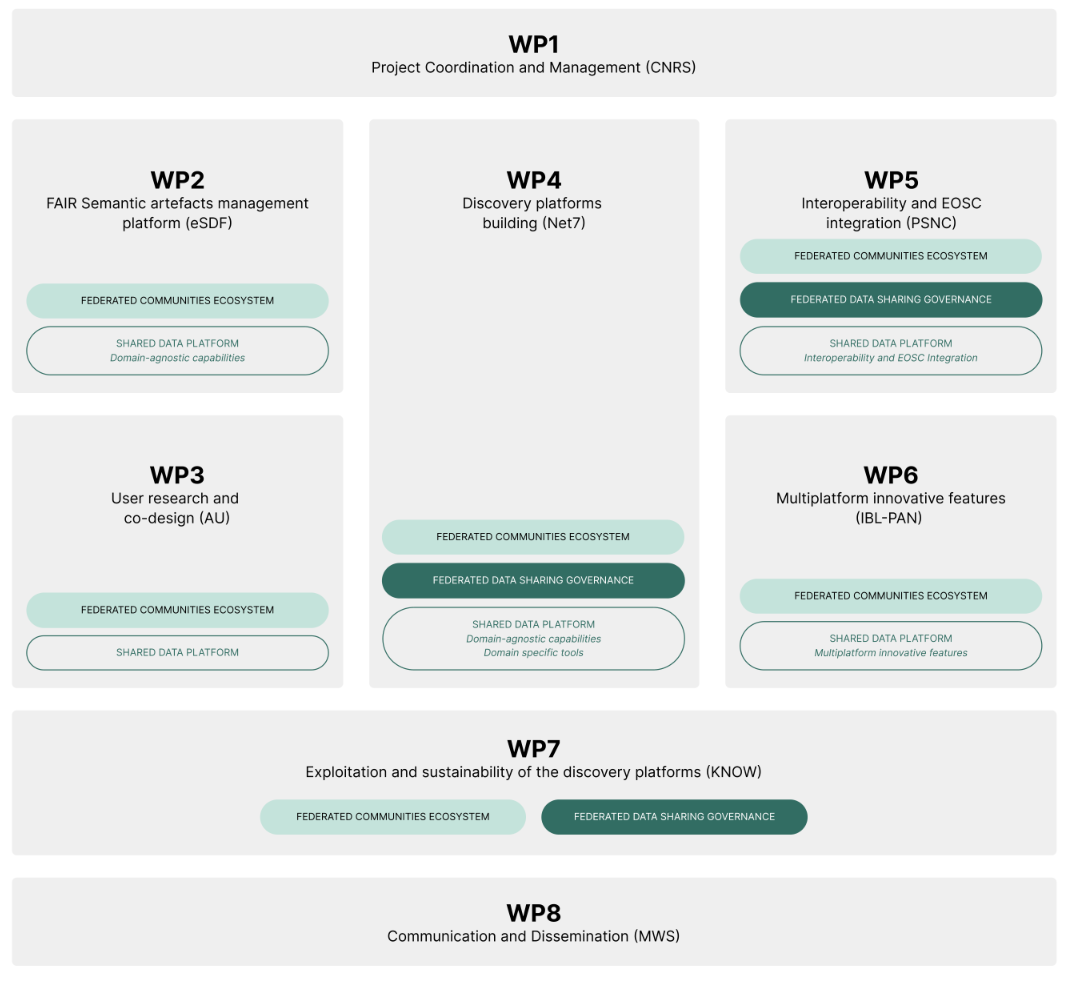
LUMEN is an interdisciplinary European project coordinated byOPERAS contributing to the expansion of the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) by building a federated discovery ecosystem for platforms across mathematics, human and social sciences, Earth sciences, and molecular dynamics, based on an innovative Data Mesh architecture.
SOUNDS OF LIFE

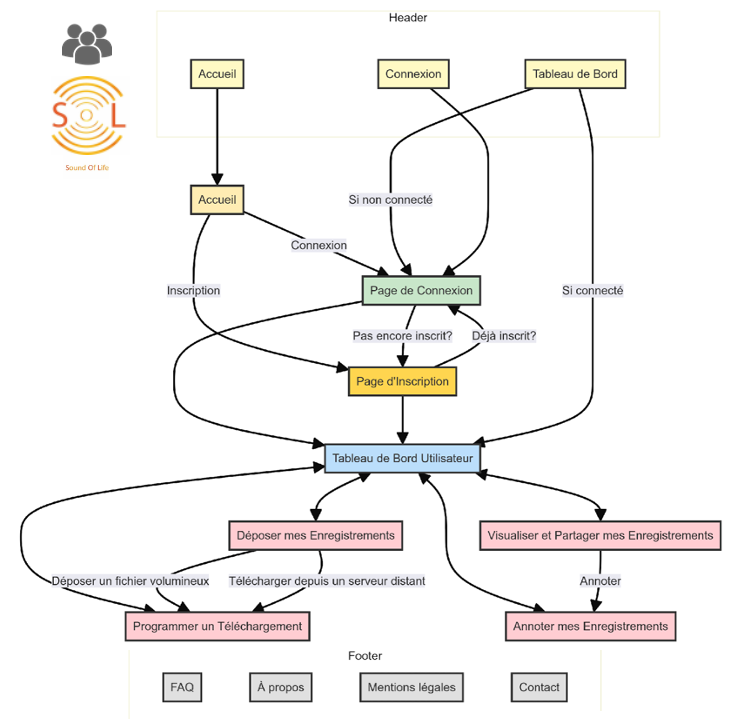
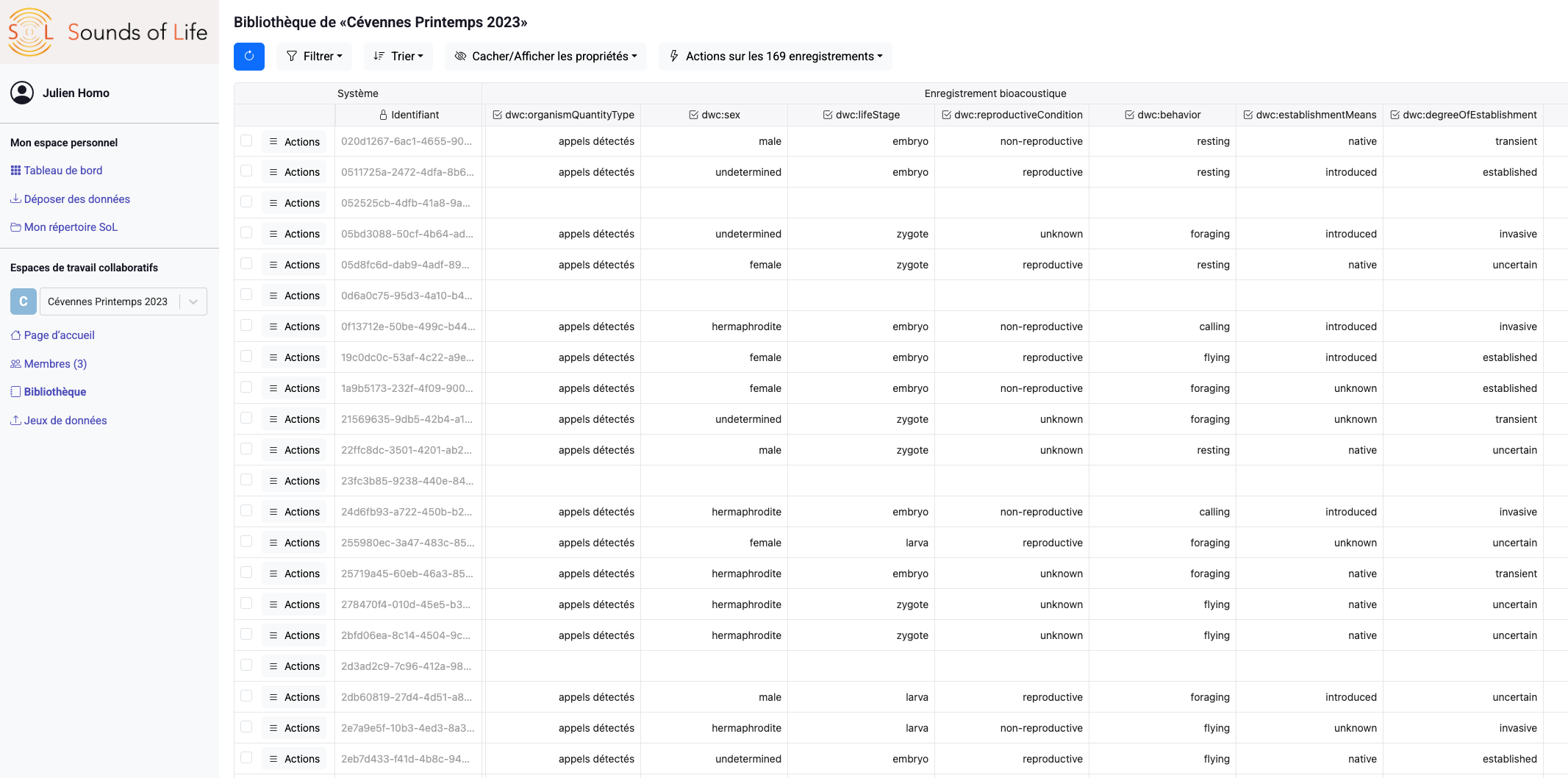
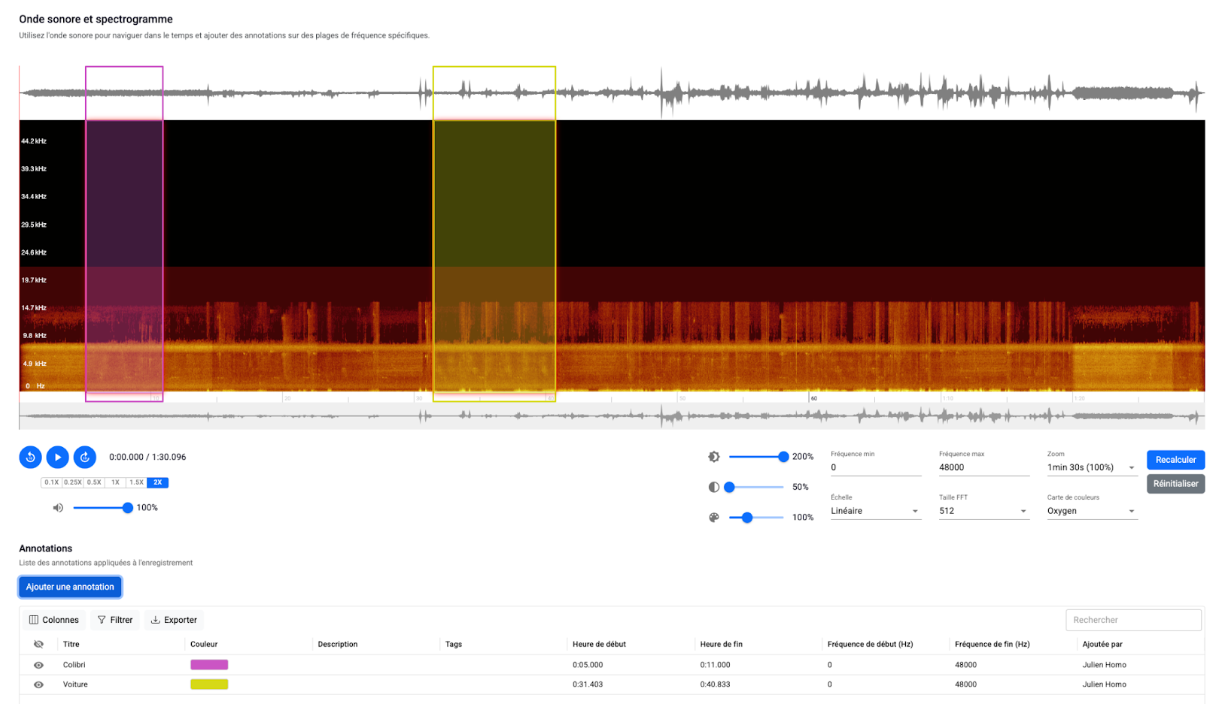
SOUNDS OF LIFE is a platform for depositing and annotating eco-acoustic recordings, developed by the Consortium Sounds of Life (MNHN, UMR Passages, INRAE, IRD…). Labeled by Huma-Num, it structures biodiversity sound data according to FAIR standards and publishes it in Darwin Core format compatible with GBIF.
Implemented using our FOXCUB DATA PLATFORM solution
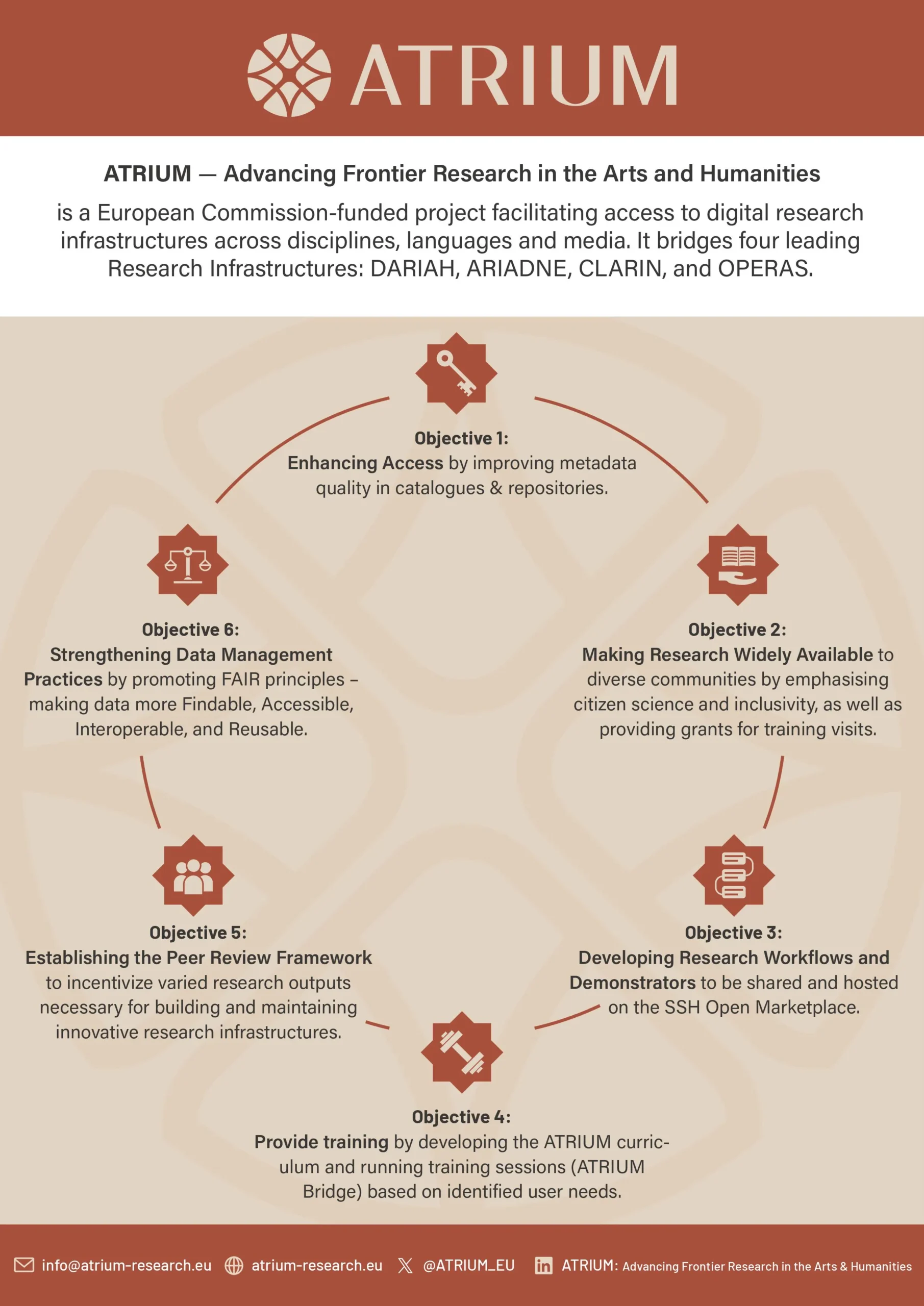
ATRIUM

ATRIUM is a European project structuring the field of digital humanities, aiming to improve the quality and interoperability of metadata at the scale of major research infrastructures (DARIAH, ARIADNE, CLARIN, OPERAS). Foxcub contributes to catalog harmonization and the collaborative enrichment of data, facilitating exchanges between platforms, researchers, and service providers.
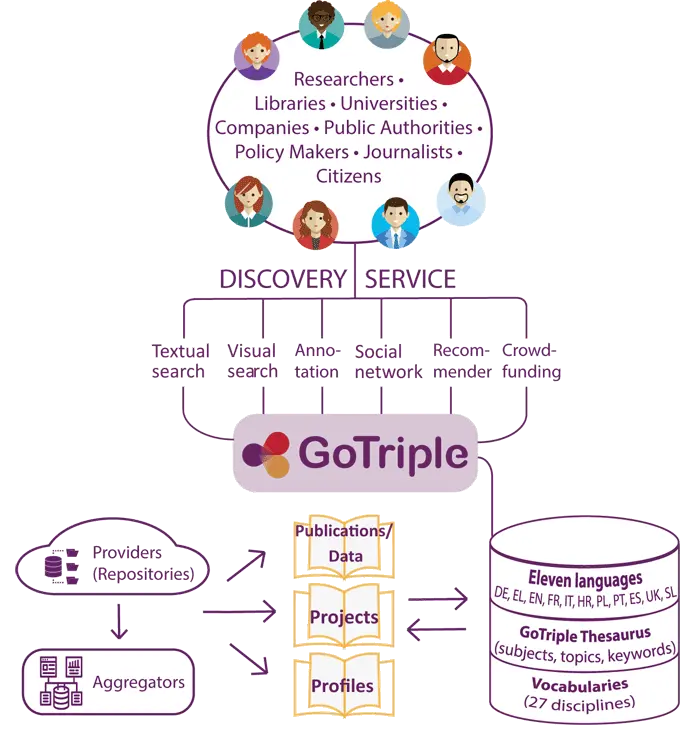
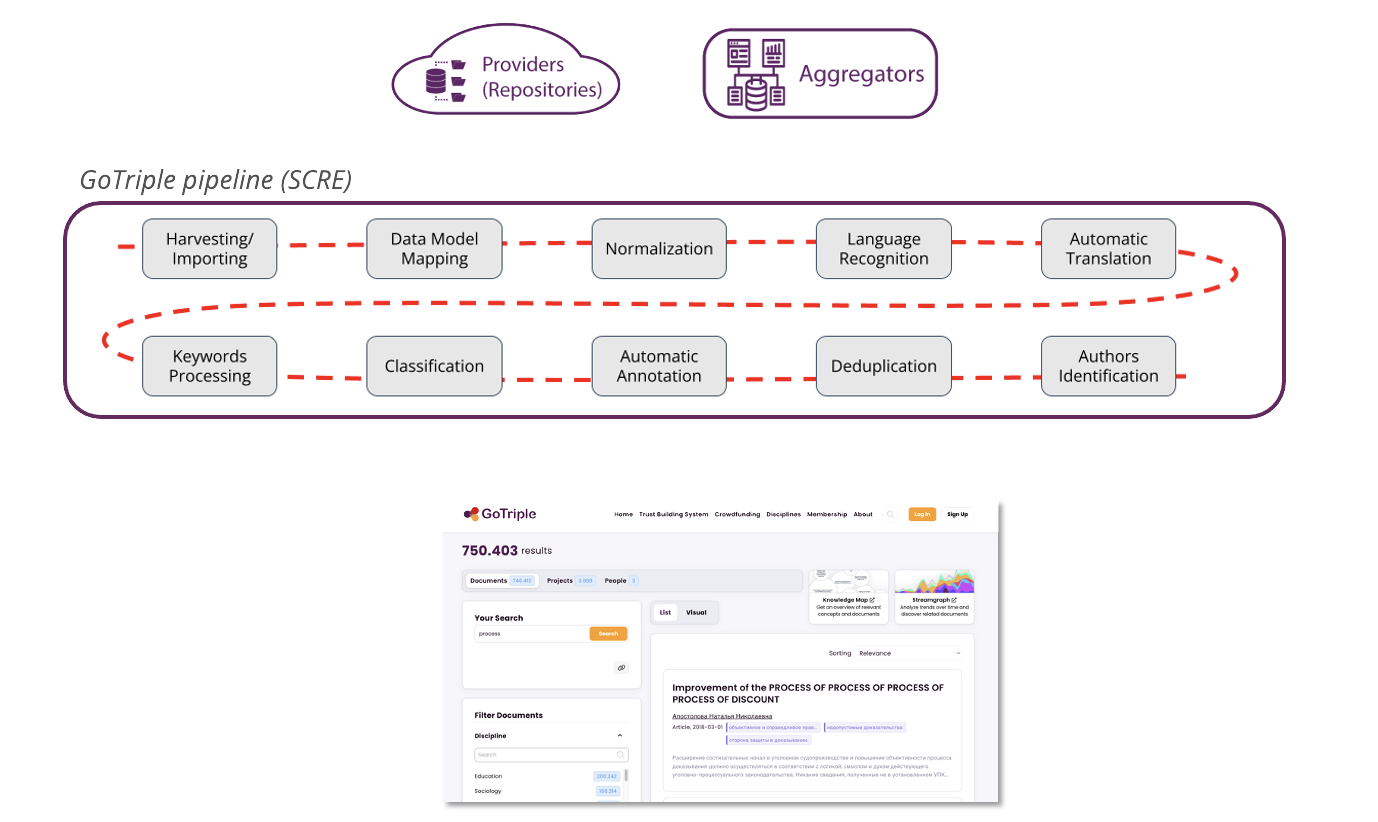
GOTRIPLE

GOTRIPLE is an innovative multilingual discovery platform for the social sciences and humanities (SSH). It is the main outcome of the European research project TRIPLE (Transforming Research through Innovative Practices for Linked Intergraduate Exploration).
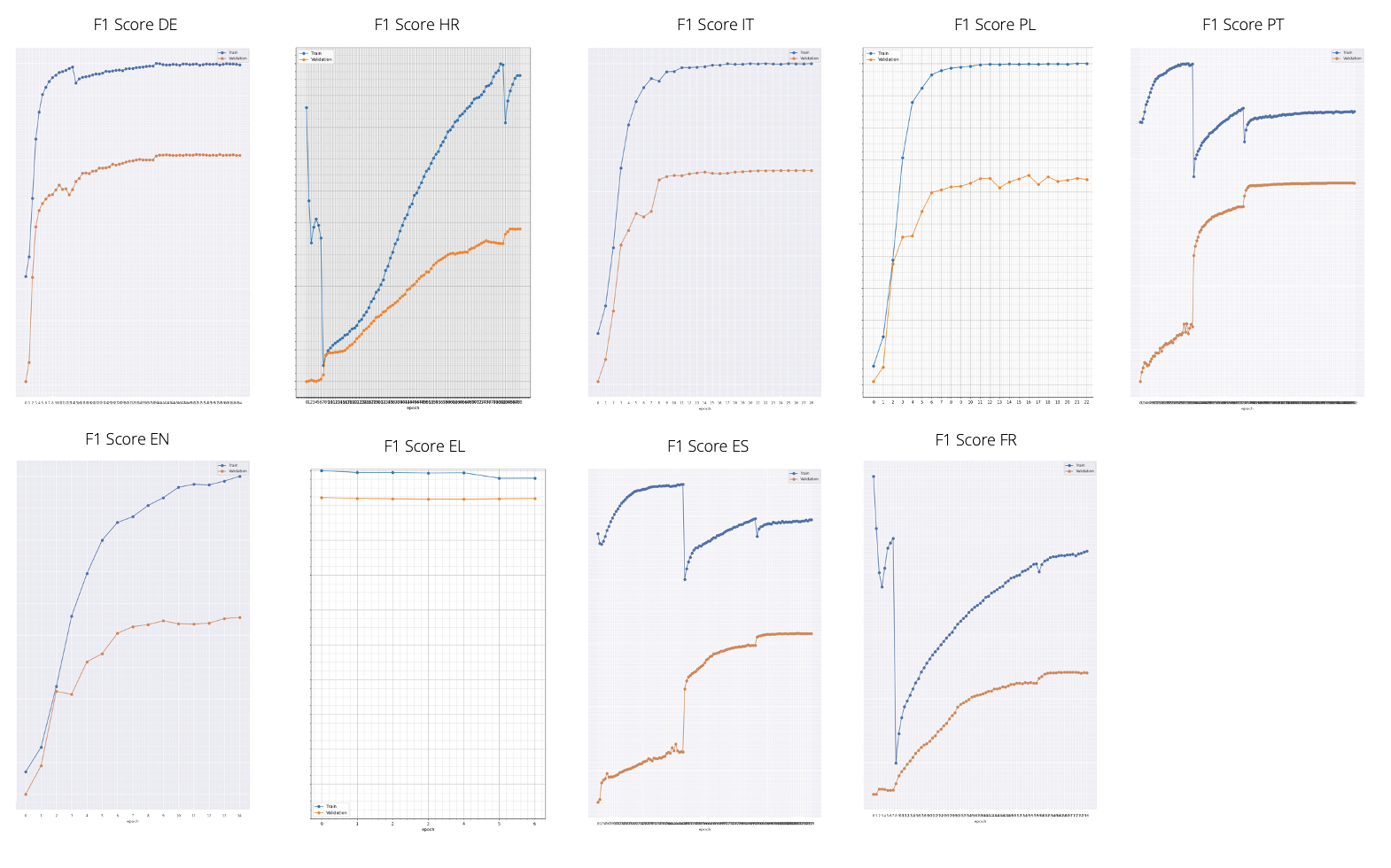
Implemented using our FOXCUB AI PLATFORM solution
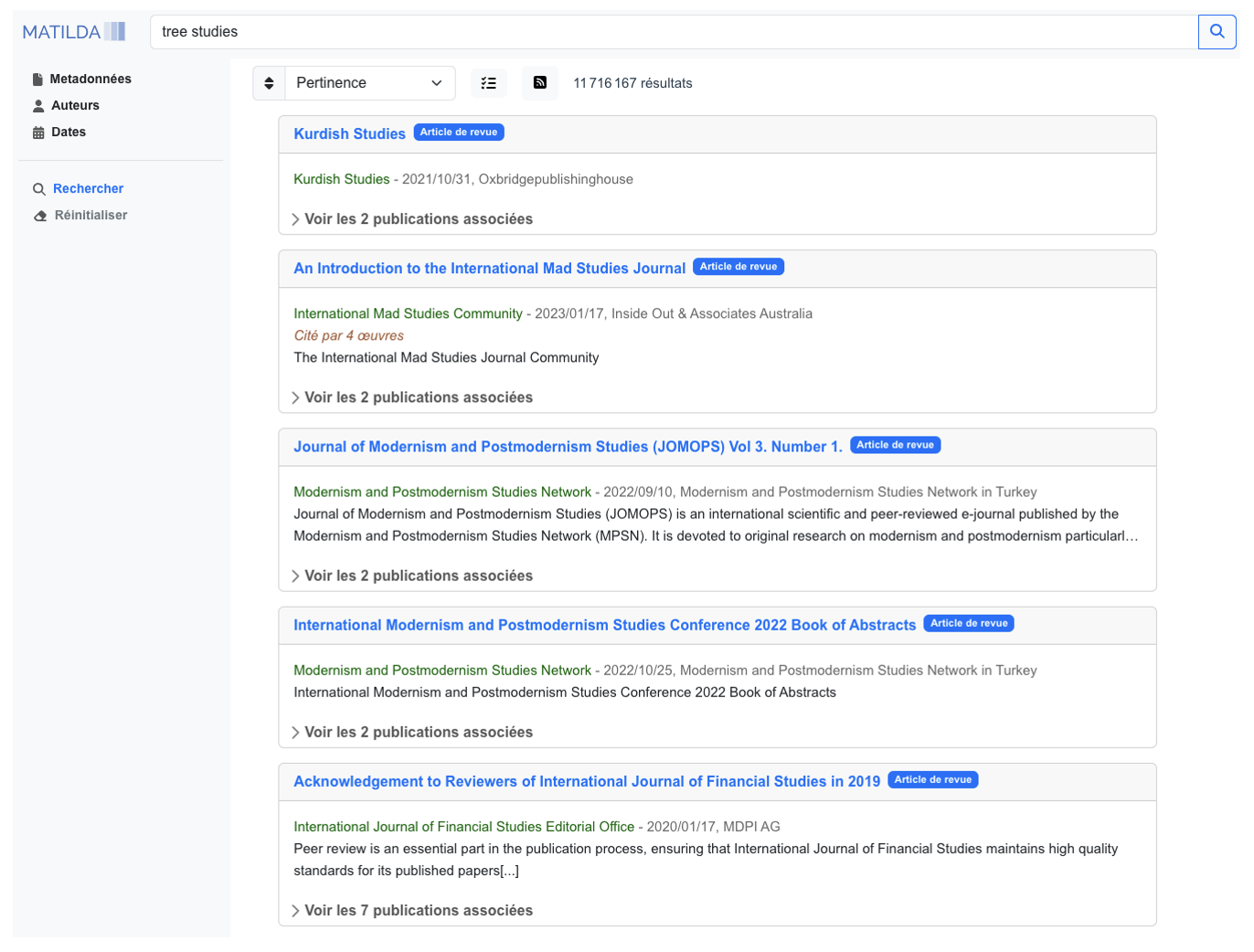
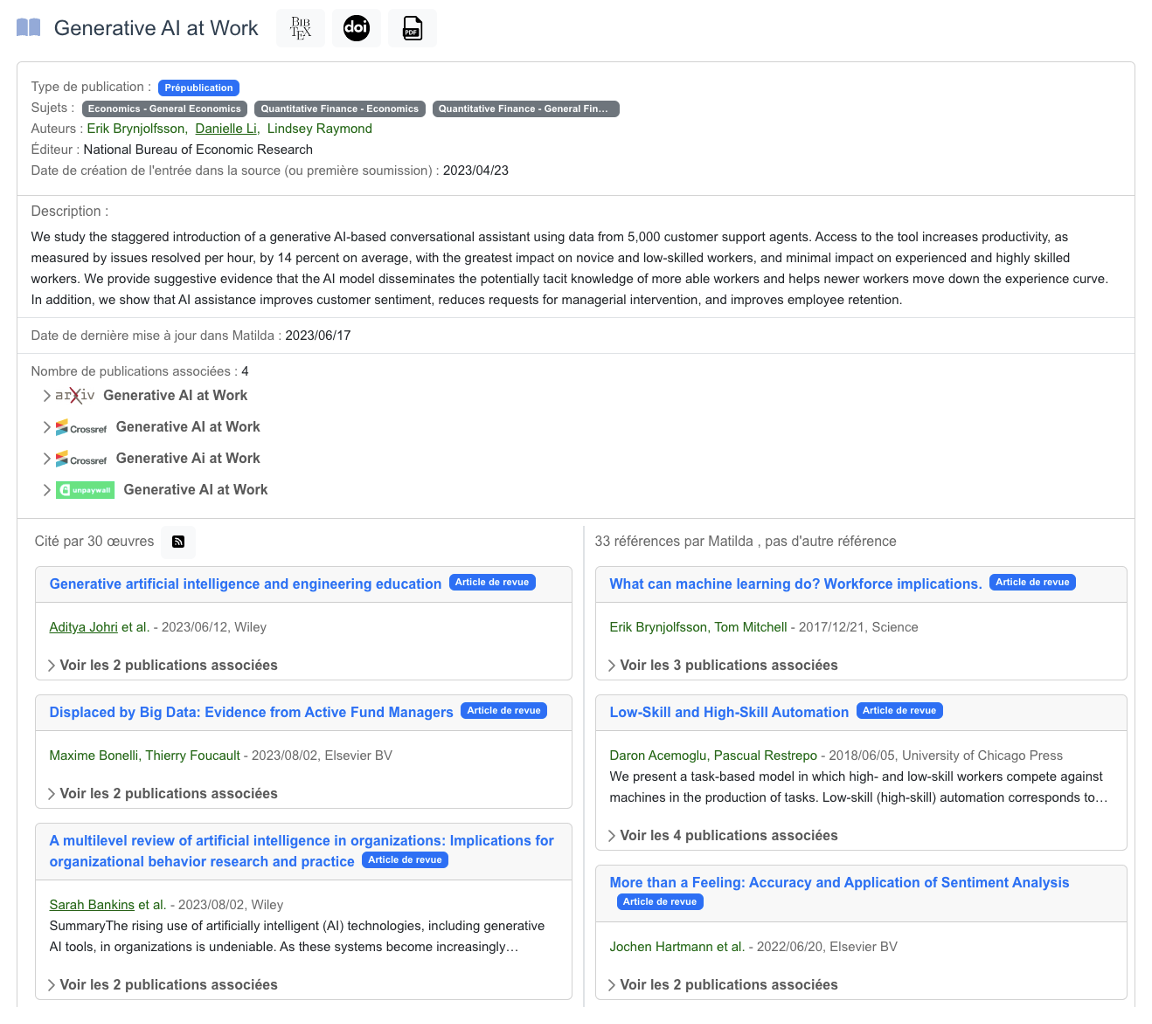
MATILDA

MATILDA is a project to develop a bibliographic and metric tool for open science, aiming to address the overlooked status of reference and citation data within the open science landscape. It is coordinated by the CNRS, the Centre de sociologie de l’innovation (I3, UMR9217) and Huma-Num (UMS 3598).
Implemented using our FOXCUB DATA PLATFORM solution
Would you like to know more? We’re available to discuss it with you.